Tugas ICT Untuk Bisnis 3: Information System In Business Today
Nama : Akhirul Annas
NIM : 1502144233
The emegence of a global economy, transformation of industrial
economies, transformation of the business enterprise, and the emergence
of digital firm make information systems essential in business today.
Information system is a fondation for conducting business today. In many
businesses, survival and the ability to achieve strategic business
goals is difficult without extensive use of information technology.
There are six reasons or objectives why businesses use information
system:
1. Operational excellence. Business improve the efficiency of their operations in order to achieve higher profitability. Information systems are important tools available to managers for achieving higher levels of efficiency and productivity in business operations. A good example is Wal-Mart that uses a RetailLink system , which digitally links its suppliers to every one of Wal-Mart's stores. as soon as a a customer purchase an item , the supplier is monitoring the item , knows to ship a replacement to the shelf.
2. New products, services, and business models. Information system is a major tool for firms to create new products and services, and also an entirely new business models. A business model describe how a company produces, delivers, and sells a product or service to create wealth.
Example: Apple inc transformed an old business model based on its iPod technology platform that included iPod, the iTunes music service, and the iPhone.
3. Customer/supplier intimacy. When a business serves its customers well, the customers generally respond by returning and purchasing more. this raises revenue and profits. The more a business engage its suppliers, the better the suppliers can provide vital inputs. This lower costs. Example: The Mandarin Oriental in Manhattan and other high-end hotels exemplify the use of information systems and technology to achieve customer intimacy. they use computers to keep track of guests' preferences, such as their preffered room temperature, check-in time, television programs.
4. Improved decision making. Many managers operate in an information bank, never having the right information at the right time to make an informed decision. These poor outcomes raise costs and lose customers. Information system made it possible for the managers to use real time data from the marketplace when making decision. Example: Verizon Corporation uses a Web-based digital dashboard to provide managers with precise real -time information on customer complains, network performance.. Using this information managers can immediately allocate repair resources to affected areas, inform customers of repair efforts and restore service fast.
5. Competitive advantage. When firms achieve one or more of these business objectives( operational excellence, new products, services, and business models, customer/supplier intimacy, and improved decision making) chances are they have already achieved a competitive advantage. Doing things better than your competitors, charging less for superior products, and responding to customers and suppliers in real time all add up to higher sales, and higher profits. Example: Toyota Production System focuses on organizing work to eliminate waste, making continues improvements, TPS is based on what customers have actually ordered.
6. Day to day survival. Business firms invest in information system and technology because they are necessities of doing business. This necessities are driven by industry level changes. Example: Citibank introduced the first automatic teller machine to attract customers through higher service levels, and its competitors rushed to provide ATM's to their customers to keep up with Citibank. providing ATMs services to retail banking customers is simply a requirement of being in and surviving in the retail banking business. Firm turn to information system and technology to provide the capability to respond to these.
Information systems are the foundation for conducting business today. In many industries, survival and even existence without extensive use of IT is inconceivable, and IT plays a critical role in increasing productivity. Although information technology has become more of a commodity, when coupled with complementary changes in organization and management, it can provide the foundation for new products, services, and ways of conducting business that provide firms with a strategic advantage.
Product Life Cycle Stages
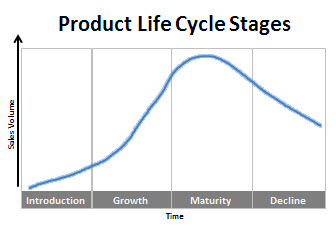
As consumers, we buy millions of products every year. And just like us, these products have a life cycle. Older, long-established products eventually become less popular, while in contrast, the demand for new, more modern goods usually increases quite rapidly after they are launched.
Because most companies understand the different product life cycle stages, and that the products they sell all have a limited lifespan, the majority of them will invest heavily in new product development in order to make sure that their businesses continue to grow.
Product Life Cycle Stages Explained
The product life cycle has 4 very clearly defined stages, each with its own characteristics that mean different things for business that are trying to manage the life cycle of their particular products.Introduction Stage – This stage of the cycle could be the most expensive for a company launching a new product. The size of the market for the product is small, which means sales are low, although they will be increasing. On the other hand, the cost of things like research and development, consumer testing, and the marketing needed to launch the product can be very high, especially if it’s a competitive sector.
Growth Stage – The growth stage is typically characterized by a strong growth in sales and profits, and because the company can start to benefit from economies of scale in production, the profit margins, as well as the overall amount of profit, will increase. This makes it possible for businesses to invest more money in the promotional activity to maximize the potential of this growth stage.
Maturity Stage – During the maturity stage, the product is established and the aim for the manufacturer is now to maintain the market share they have built up. This is probably the most competitive time for most products and businesses need to invest wisely in any marketing they undertake. They also need to consider any product modifications or improvements to the production process which might give them a competitive advantage.
Decline Stage – Eventually, the market for a product will start to shrink, and this is what’s known as the decline stage. This shrinkage could be due to the market becoming saturated (i.e. all the customers who will buy the product have already purchased it), or because the consumers are switching to a different type of product. While this decline may be inevitable, it may still be possible for companies to make some profit by switching to less-expensive production methods and cheaper markets.
Product Life Cycle Examples
It’s possible to provide examples of various products to illustrate the different stages of the product life cycle more clearly. Here is the example of watching recorded television and the various stages of each method:- Introduction - 3D TVs
- Growth - Blueray discs/DVR
- Maturity - DVD
- Decline - Video cassette
However, the key to successful manufacturing is not just understanding this life cycle, but also proactively managing products throughout their lifetime, applying the appropriate resources and sales and marketing strategies, depending on what stage products are at in the cycle.

Comments
Post a Comment